Get interesting information about Why Are Plants More Difficult To Make Into Transgenic Species, this article is specially curated for you from various reliable sources.

Why are Plants More Difficult to Make into Transgenic Species?
In the realm of genetic engineering, creating transgenic species has become a common practice. From manipulating the genes of animals to enhancing crop yields, scientists have made significant strides in this field. However, when it comes to plants, the process of genetic modification presents unique challenges. Unlike animals, plants possess a complex genetic makeup that often hinders the successful introduction and expression of foreign genes.
In this article, we delve into the intricate world of plant genetic engineering, exploring the reasons why plants are more difficult to make into transgenic species. We shed light on the challenges faced by scientists, the latest advancements in the field, and provide valuable tips for aspiring biotechnologists.
The Complexity of Plant Genomes: A Maze of Challenges
One of the primary reasons why plants are more difficult to make into transgenic species is the sheer complexity of their genomes. Plant genomes are often much larger and more complex than those of animals. For example, the rice genome consists of approximately 430 million base pairs, while the human genome contains only about 3 billion base pairs.
This vast difference in size poses a significant challenge for scientists attempting to introduce foreign genes into plants. Finding the correct location to insert the genes without disrupting the plant’s normal function is like searching for a needle in a haystack. Additionally, the presence of multiple copies of genes within the plant genome can further complicate the process.
The Epigenetic Puzzle: A Hidden Layer of Complexity
Beyond the challenges posed by the sheer size and complexity of plant genomes, another factor that makes genetic engineering in plants more difficult is the phenomenon of epigenetics. Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence itself. These changes can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as environmental cues or the plant’s developmental stage.
Epigenetic modifications can have a profound impact on the expression of foreign genes in transgenic plants. For example, if a foreign gene is inserted into a region of the genome that is epigenetically silenced, it may not be expressed at all. This can make it difficult to obtain consistent and predictable results when creating transgenic plants.
The Power of Plasmids: A Tool with Limitations
Scientists often use plasmids, small circular DNA molecules, to introduce foreign genes into plants. Plasmids are able to replicate independently of the plant’s genome, making them a convenient tool for genetic engineering. However, the use of plasmids is not without its limitations.
One major limitation is that plasmids can be unstable in plants. They can be lost during cell division or become integrated into the plant’s genome in an unpredictable manner. This can lead to unexpected changes in gene expression and can make it difficult to create stable transgenic lines.
Emerging Technologies: A Glimmer of Hope
Despite the challenges, advances in genetic engineering techniques are offering new hope for plant transformation. Gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 allow scientists to make precise changes to the plant’s genome, overcoming some of the limitations of traditional genetic engineering methods.
Additionally, the development of new plant transformation vectors, such as binary vectors, has improved the efficiency and stability of gene transfer. These vectors are designed to minimize the risk of plasmid loss and integration into the plant genome, resulting in more predictable and reliable transgenic plants.
Tips for Successful Plant Transformation: A Guide for Biotechnologists
For aspiring biotechnologists working with plant genetic engineering, here are a few tips to enhance your success:
- Choose the right target gene: Careful selection of the target gene is crucial. Consider the gene’s function, expression pattern, and potential impact on the plant’s phenotype.
- Optimize the transformation method: Different transformation methods have varying efficiency and applicability. Experiment with different methods to determine the one that yields the best results for your specific plant species.
- Use appropriate selection markers: Selection markers allow you to identify transgenic plants that have successfully integrated the foreign gene. Choose markers that are easy to screen for and that do not interfere with the plant’s growth and development.
- Monitor gene expression: Once you have created transgenic plants, it is important to monitor the expression of the foreign gene. This will help you determine if the gene is being expressed at the desired level and in the appropriate tissues.
- Collaborate with experts: If you encounter challenges or have specific questions, do not hesitate to seek advice from experienced scientists in the field. Collaboration can accelerate your research and provide valuable insights.
FAQs: Demystifying Plant Transformation
Q: Why are plants harder to make into transgenic species than animals?
A: Plants have complex genomes, epigenetics, and a greater dependence on environmental factors, making the introduction and expression of foreign genes more challenging.
Q: What are the latest advancements in plant transformation?
A: Gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 and the development of new plant transformation vectors have improved the efficiency and precision of genetic modifications in plants.
Q: How can I improve my success in plant transformation?
A: Optimize the transformation method, carefully select the target gene, use appropriate selection markers, monitor gene expression, and collaborate with experienced scientists.
Conclusion: A Call for Collaboration and Innovation
Creating transgenic plants is a complex and challenging endeavor, but one that holds immense potential for improving agriculture, medicine, and other fields. As we unravel the intricacies of plant genomes and develop new technologies, we are making strides towards creating transgenic plants that can meet the needs of a growing global population.
We encourage researchers, biotechnologists, and scientists to continue exploring the frontiers of plant genetic engineering. Through collaboration, innovation, and a deep understanding of plant biology, we can unlock the vast potential of this transformative field.
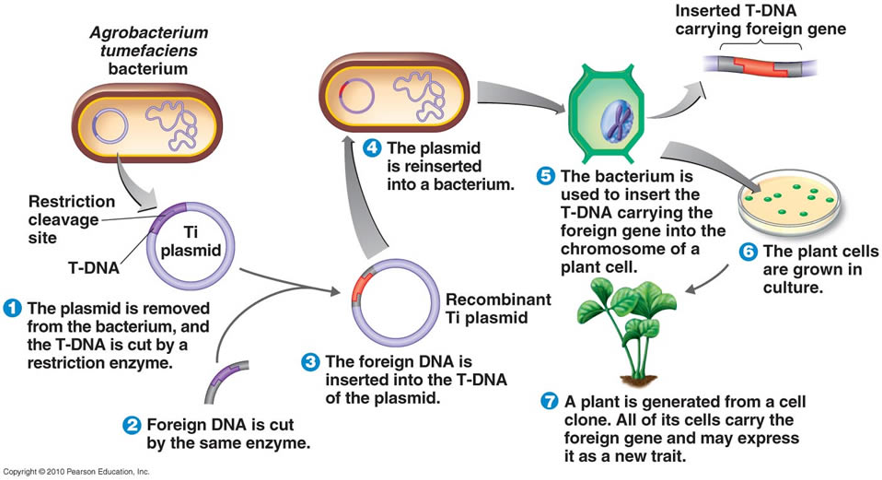
Image: getchancegetchange.blogspot.com
We express our gratitude for your visit to our site and for reading Why Are Plants More Difficult To Make Into Transgenic Species. We hope this article is beneficial for you.